Groups of lung diseases that cause severe lack of oxygen are considered chronic obstructive pulmonary diseases or COPD. Chronic bronchitis and emphysema are the most common COPD conditions. Chronic bronchitis is an inflammation of the lining of your bronchial tubes. These tubes carry air to and from your lungs. Emphysema develops when the air sacs or alveoli in your air passages are destroyed.
COPD damage to your lungs cannot be reversed, but there are treatments that can control symptoms and minimize further harm.
Symptoms
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease symptoms do not appear until there is irreversible damage to the lungs. As time goes on, this damage will worsen and symptoms will be noticeable. Chronic bronchitis symptoms include:
- A cough that you have for at least three months during the year;
- Shortness of breath during physical activities;
- Wheezing all the time;
- Chest tightness;
- Clearing your throat all the time and particularly first thing in the morning;
- A chronic cough that produces clear, white or yellow sputum
- Blue fingernail beds or cyanosis;
- Respiratory infections;
- Fatigue;
- Weight loss.
You may also experience episodes or exacerbations where symptoms persist for days or weeks.
Emphysema caused COPD often begins with smoking or being exposed to fumes from burning fuel used for cooking and heating. It is estimated that about 20 percent of chronic smokers develop COPD and other lung conditions.
Causes
Your windpipe, trachea, or two large bronchi or tubes are the passageways for air to travel to your lungs. The bronchi divide into branches and smaller tubes that end in clusters of air sacs or alveoli. These sacs are very thin and full of capillaries. When oxygen passes into these capillaries carbon dioxide is expelled out of your body. The delicate dance depends on the natural elasticity of the bronchial tubes and air sacs to force carbon dioxide out of the body. If you are suffering from COPD these tubes and sacs lose elasticity and collapse. This leaves air trapped in your lungs.
Causes of airway obstruction
When you have emphysema the fragile walls of your alveoli are destroyed and small airways collapse when you exhale. This causes carbon dioxide to remain in your lungs.
Chronic bronchitis happens when your bronchial tubes are inflamed, narrowed and your lungs produce mucus. Mucus secretions block the narrowed bronchi tubes which causes chronic coughing.
Cigarette smoke and other environmental irritants cause lung damage that leads to COPD. There may also be other factors that cause cigarette smoke to be a part of COPD. These can be a genetic susceptibility to the disease or secondary infections. If you are exposed to second hand smoke, cigar and pipe smoke, air pollution and dust and fumes in the workplace you are susceptible to COPD.
There is a genetic disorder that can cause low level of alpha-1-antitrypsin or a protein make in the liver and secreted into the bloodstream to protect the lungs. A deficiency of this protein will cause damage to the liver and bring on COPD. You can be treated by medically replacing the missing protein.
Complications
If you are diagnosed with COPD you may experience complications that include:
- Respiratory infestations such as the cold, flu and pneumonia. If you have a respiratory infection you will have a difficult time breathing and further damage to the lung tissues occur. Those with COPD need to receive annual flu vaccinations and immunizations against pneumococcal pneumonia.
- COPD causes high blood pressure in the arteries that carry blood to the lungs. This is pulmonary hypertension.
- If you are suffering from COPD you may have an increase in heart disease and heart attacks.
- Lung cancer is a very real complication of COPD. If you are a smoker with chronic bronchitis you will have a high risk of developing lung cancer.
- Depression is a direct consequence of COPD. Difficulty breathing keeps you from your normal activities. Any serious illness will contribute to depression. Talk to your physician if you feel unusually sad or helpless.
Medications
There are medications that can be used to help treat the symptoms and complications of COPD. Medications can be either long term or as needed.
- Bronchodilators are medications that are released through an inhaler. They reduce the swelling in the muscles around the airways. This is designed to get rid of coughing and shortness of breath. If you have severe COPD you will need fast-acting bronchodilator before activities and a long-lasting form during the day and night.
Short acting medications used in a bronchodilator include albuterol, levalbuterol, and ipratropium. Those medications that are for long term use in a bronchodilator include tiotropium, salmeterol, formoterol, arformoterol, and aclidinium.
- Inhaled corticosteroid medications will reduce airway inflammation and prevent exacerbations. You may have bruising and oral infections however with inhaled corticosteroids.
- Oral steroids can be used for those who have moderate to severe exacerbation. These medications are known to avert further deterioration of COPD symptoms, but they do have very severe side effects. Diabetes, weight gain, cataracts, and infection risks are only a few of the side effects of oral steroids.
- Phosphodiesterase-4 inhibitors are a new medication that is approve for those with very severe COPD. This mediation decreases airway inflammation and relaxes the airways. You may have diarrhea and weight loss with long term use of these mediations.
- For respiratory infections like pneumonia and acute bronchitis, antibiotics will fight the exacerbations.
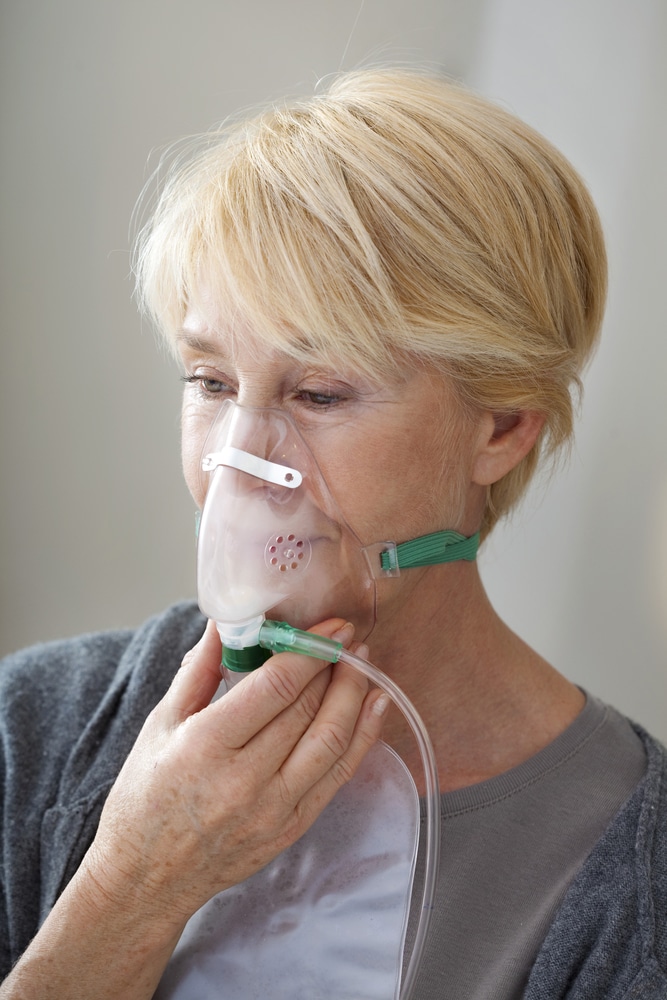
- You can also have oxygen therapy if you do not have enough oxygen in your blood. You can use light weight and portable oxygen units that help you get enough oxygen or you will be required to use larger units of oxygen on a daily basis.
- Pulmonary rehabilitation programs will include education, training, nutrition and counseling. You may find that this type of treatment works well and keeps your nutrition and health needs at a high level.
- Surgery can be an option for those with severe emphysema who cannot be helped by medications. This includes lung volume reduction surgery. Wedges of damaged lung tissues are removed to create extra space in your chest cavity. This will help the diaphragm and remaining lung tissues work efficiently.
- Lung transplant surgery may be an option if you meet specific criteria. Transplants can improve your ability to breathe and be active. It is however a very serious operation that can bring on significant risks. You will have to be on immune-suppressing medications for the rest of your life or suffer the pain of rejection.
Home remedies
Take care of yourself and your health. Learn breathing techniques plus breathing positions and relaxation methods. Mucus tends to collected in airways and you will need to drink plenty of water, use a humidifier and use controlled coughing to clear airways.
Exercise regularly. It might seem a bit difficult to exercise when you cannot breathe, but you can improve your overall strength and endurance by exercising.
A healthy diet is very important to keep up your strength. If you are underweight you may be prescribed nutritional supplements. Being overweight will require you to lose significant weight to help your breathing.
Do avoid smoke and air pollution. Second hand smoke contributes to lung damage. Do stay away from areas where air pollution and smoking irritates your lungs.
Keep your regular appointments, monitor your lung functions and get your annual flu vaccine. Living with COPD is a challenge particularly as it becomes harder to catch your breath. You may have to give up activities you previously loved, and learning to live with COPD will be a lifelong requirement.