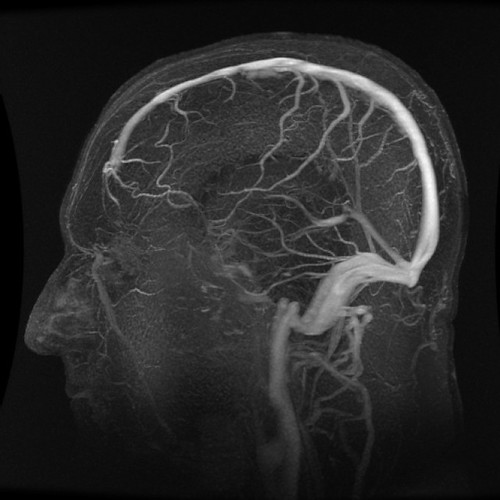
A cerebrovascula accident or stoke occurs when blood supplies to the brain are disrupted. This causes brain cells to die. Some of the causes of a stroke include narrowing of the small arteries in the brain or hardening of the arteries leading to the brain.
If you feel you or believe someone else is experiencing a stroke, immediate emergency medical attention is imperative. Call 911 or go to an emergency room to confirm the diagnosis. Urgent medical decisions are needed to decide whether clot busting drugs need to be administered to reverse the effects of a stroke. A very small window from the beginning of symptoms to using clot busting therapy is available; perhaps only minutes. If there are delays, the opportunity to intervene is gone.
What You Should do in the Event of a Stroke
Immediate medical attention is necessary to prevent depilating and long lasting effects of a stroke. If you call first for an ambulance and while waiting for the paramedics or EMTs the following first aids may help.
- Have the affected person lie flat. This promotes an optimal blood flow to the brain.
- If unresponsiveness or nausea are present, roll the affected person on their side to prevent vomiting or choking.
- If the patient has been taking aspirin to prevent strokes, stop administering aspirin immediately.
If you suspect a stroke, follow CPSS or the Cincinnati Prehospital Stroke Scale. This includes smiling and ensuring that the face is moving symmetrically, raising both arms above the head and watching for weakness on either side of the body, speaking a simple sentence. If any of these actions cannot be performed, call 911 immediately.
Causes
Blockage of an artery or blood vessel can cause stroke. A single vessel can disturb a very small area of the brain and affected tissues will die.
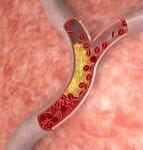
- Atherosclerosis or hardening of the arteries heading to the brain will cause a stroke. Four main blood vessels provide the brain with blood and perform the following duties:
- The anterior circulation of the brain that controls motor abilities, sensation, speech, thought and motion is supplied by the carotid arteries.
- Posterior circulation supplies the brainstem and the cerebellum that controls automatic brain function and coordination. This includes breathing.
- Embolisms from the heart to the brain cause strokes. These are blood clots that form within the heart, break off and travel through the arteries to the brain.
- Cerebral hemorrhages or bleeding within the brain cause stroke. The most common reason for brain bleeding is high blood pressure, aneurysms and arteriovenous malformations. Malformations are blood vessels that are weak and break.
- Obstruction of an artery by thrombosis or a clot is the most common reason for a stroke. The portion of the brain that is supplied by the clotted vessel is deprived of blood and oxygen. The cells begin to die and that part of the brain stops functioning.
Types of Strokes
Emboli stroke is due to calcium and cholesterol buildup on the walls of the arteries or heart (atherosclerotic plaque) breaking away from the walls. The clot travels thought the bloodstream and houses in an artery located either in or near the brain. A blood clot might form in a heart chamber as the result of an irregular heartbeat, break off, travel, and form a plug. This type of stroke can be caused by the large arteries or small veins in the brain.
Cerebral Hemorrhage
A cerebral hemorrhage occurs when blood vessels in the brain rupture and bleed into the surrounding tissues. Again the brain is depleted of oxygen and swelling or cerebral edemas form. Swelling causes the brain to squeeze against the skull.
Subarachnoid Hemorrhage
Blood accumulates beneath the arachnoid membrane that lines the brain. The blood can originate from an abnormal blood vessel that is leaking or has ruptured. This can be from an aneurysm. These types of hemorrhages cause sudden and severe headaches, vomiting and nausea, inability to tolerate light, and a very stiff neck. If not treated major neurological damage, comas, or brain death can occur.
Vasculitits is a rare condition that can cause stroke. Blood vessels become inflamed and cause deceased blood flow to the brain.
Migraine Headaches
There is a slight increase in occurrence of stokes by those who suffer with migraine headaches. These headaches set off narrowing of the main blood vessels in the brain. Migraines often mimic stokes. There may be loss of function only on a single side of the body plus vision or speech problems transpire with sever migraines. Symptoms usually resolve within 24 hours.
Transient Ischemic Attacks (TIA)
TIAs are short lived and almost mini strokes. TIAs cause temporary impairment of brain function, but do get better and resolve within 24 hours. A TIA is caused by loss of blood supply to the brain by a clot that spontaneously forms. Treat these types of “mini” strokes as medical emergencies. There is no guarantee that they will resolve on their own and medical intervention may be necessary. If you suffer from double vision, dizziness, weakness on one side of your body or sever loss of balance plus paralysis of any part of your body you may be experiencing transient ischemic attacks.
Symptoms
When brain cells are deprived of oxygen, cells begin to die and stop performing their duties. You can have a small stroke that damages brain tissues and not have any physical symptoms. These “silent” strokes cannot be detected but may be the precursors to larger strokes. Watch for signs of stroke that may include:
- Weakness or numbness in one side of the body that include the face, leg or arm. Loss of voluntary movement and sensation can be total or partial; watch for tingling sensations in the area.
- Confusion or trouble speaking or understanding what is going on around you is a symptom.
- You may also experience excessive drooling.
- If you have immediate trouble in seeing from one or both eyes, check it out.
- Loss of balance or coordination plus dizziness.
- Severe and sudden headaches with no known cause.
Treatments
Using alteplase or TPA as a clot-buster drug can dissolve the blood clot contributing to the stroke. There is a very small window to use this drug which makes getting medical attention quickly, imperative.
Aspirin and heparin are drugs used to thin the blood and prevent clots. These can be used in treating stroke patients and providing speedy recovery. These types of medications can improve the outcome from a current stroke and prevent subsequent strokes.A stoke patient”s blood pressure will be controlled and monitored in the event of a stroke. If the stroke is ischemic or hemorrhagic intravenous medications for high blood pressure can help alleviate some of the symptoms of stroke.
Supplemental oxygen is always provided.
If you are a diabetic blood sugar or glucose levels will be continually checked. Your glucose levels increase after a stroke and providing glucose lowering medication may minimize the severity of a stroke.
Prevention
Controlling risk factors greatly decreases the risk of strokes. High blood pressure or pressures greater than 130/85 will need to be managed with medications and life style changes.
Stop smoking to reduce risk of strokes. Chemicals in cigarettes are known to be a major factor in the development of atherosclerosis or narrowing of the arteries in the body.
Diabetes causes small vessels to close prematurely. If these blood vessels close in the brain you may have small strokes that lead up to large, damaging strokes.
High cholesterol and triglycerides in the bloodstream are potential causes of strokes. Fats caused by cholesterols will eventually block blood vessels and develop plaques.
Prescriptions of warfarin or blood thinner can potentially stop strokes from happening. Those with atrial fibrillation or irregular heartbeats often have blood clots that break off and travel to the brain. Aspirin may also be used for anticoagulation in atrial fibrillation patients.
Anti platelet therapy drugs can decrease clotting risks and reduce the rise of strokes. These medicines act on platelet and decrease their tendency to form blood clots. There is an increased risk of bleeding internally, however with these type of medications.
What are Strokes?
The unexpected death of brain cells due to deficiency of oxygen and blockages of blood flow or breach in an artery in the brain bring about strokes. If you have sudden tingling, weakness or paralysis only in a portion of your body and you are having difficulty swallowing, seeing or walking, get to an emergency room immediately. Do minimize your risk of strokes by taking care of high blood pressure, cholesterol levels, stop smoking immediately and controlling your diabetes.